Table of Contents
ToggleImagine biting into a perfectly sculpted pizza that looks like a work of art. Welcome to the world of 3D food printing, where culinary dreams take shape—literally! This innovative technology is revolutionizing the way we think about food, turning everyday meals into personalized masterpieces.
What Is 3D Food Printing?
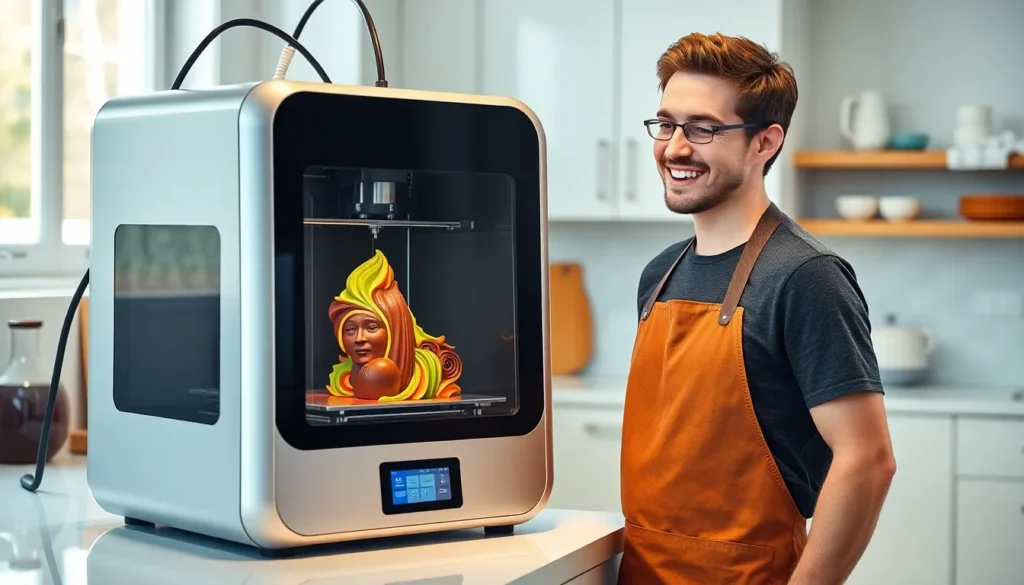
3D food printing is an advanced technology that creates food items layer by layer, using digital files as templates. This innovative process utilizes food materials like purees, doughs, and other edible substances, allowing chefs and food designers to craft intricate designs. Artists in the culinary field can leverage 3D food printers to push the boundaries of traditional food presentation.
Manufacturers use specialized nozzles to extrude food ingredients, which solidify into the desired shapes. Some printers enable customization, allowing users to alter flavors, textures, and nutritional content according to personal preferences. Notable examples include chocolate sculptures, pasta figures, and even pizzas that showcase unique designs.
Researchers emphasize the environmental benefits of 3D food printing. By minimizing food waste, the technology aligns with sustainable practices. It can utilize ingredients considered unusable or unwanted, transforming them into appealing dishes.
Culinary schools increasingly integrate 3D food printing into their curriculums. Students experiment with creating edible art and explore the science behind food textures and flavors. This educational aspect plays a crucial role in shaping the future of food innovation.
Various industries are adopting 3D food printing. Restaurants use it to enhance customer experiences with personalized dishes, while food manufacturers explore production efficiencies. Chefs find that the technique not only saves time but also inspires creativity in the kitchen.
How 3D Food Printing Works
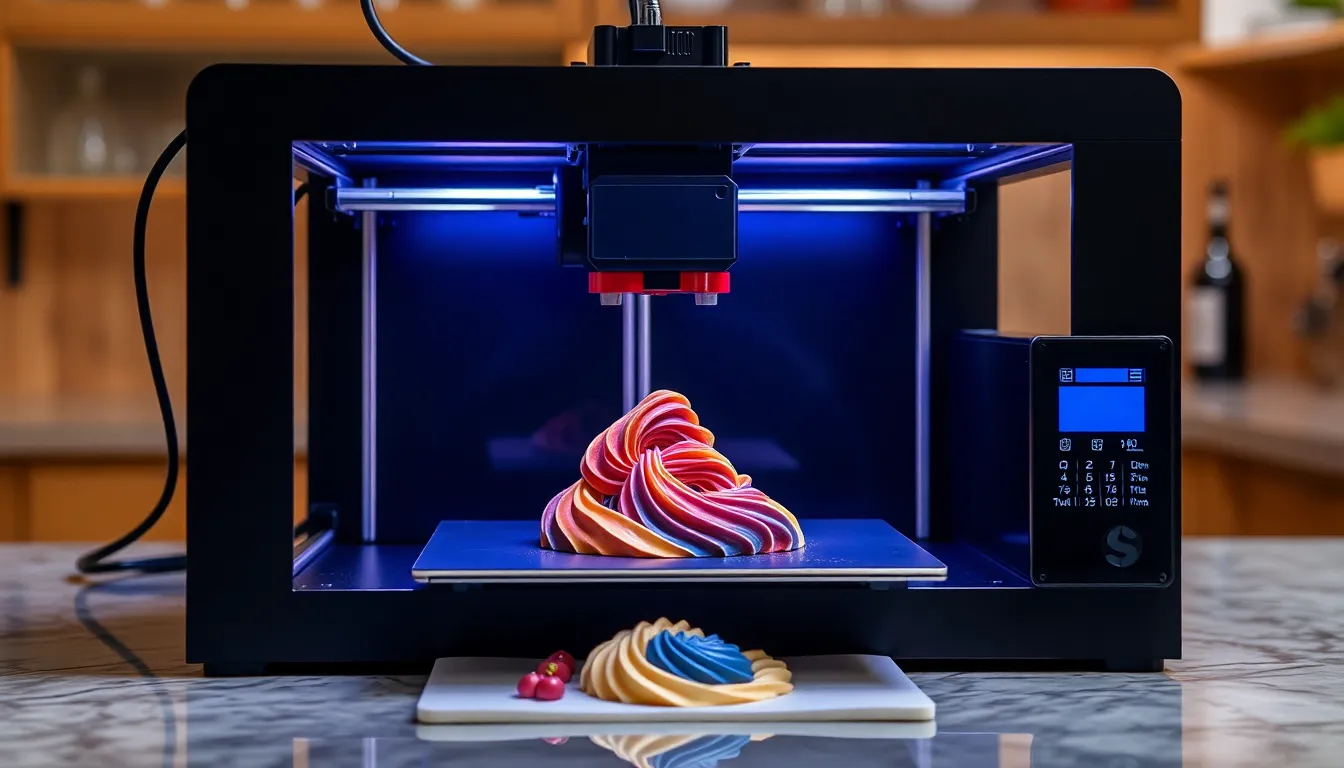

3D food printing combines technology and culinary arts, creating a new method of food preparation. It employs specialized printers that layer materials to create intricate designs.
The Technology Behind 3D Food Printing
Advanced technology powers 3D food printing. Printers utilize a computer program that generates digital templates. These templates guide the printer, directing the deposition of ingredients layer by layer. Thermal extrusion, binder jetting, and inkjet printing are common methods employed. These techniques allow for precision in food crafting. Custom designs emerge from this technology, transforming conceptual ideas into edible art.
Materials Used in 3D Food Printing
Various materials contribute to the 3D food printing process. Common ingredients include chocolate, dough, and pureed fruits and vegetables. These materials undergo preparation, often in paste form, enabling them to flow through the printer’s nozzle. Unique combinations of ingredients create diverse textures and flavors. Chefs can also use alternative proteins and sugars to enhance nutritional profiles. This flexibility in material choice fosters creativity and encourages personalized culinary experiences.
Benefits of 3D Food Printing
3D food printing offers various advantages that transform culinary experiences. Significant benefits include customization and sustainability.
Customization and Personalization
Customization features prominently in 3D food printing. Chefs can create unique dishes tailored to individual preferences. This approach enhances flavor profiles by mixing different ingredients. Dietary restrictions or allergies can easily be accommodated, allowing for personalized meals. Personalized shapes and designs achieve aesthetic appeal, making meals visually striking. Furthermore, 3D technology enables quick adjustments during the printing process, yielding on-demand creations that cater to specific tastes. Unique designs foster a sense of ownership over the dining experience, making each meal special.
Sustainability Aspects
Sustainability represents another critical advantage of 3D food printing. The technology minimizes food waste by utilizing ingredients that might otherwise go unused. Chefs can repurpose surplus fruits and vegetables into new food forms, reducing landfill contributions. Food printers also use precise amounts of ingredients, cutting down on excess. This practice optimizes resource efficiency while maintaining quality and flavor. Additionally, 3D food printing encourages local sourcing of ingredients, shortening supply chains and reducing carbon footprints. Emphasizing sustainability aligns culinary practices with environmental responsibilities, paving the way for a greener future in food production.
Applications of 3D Food Printing
3D food printing showcases versatility across various fields, enhancing culinary experiences and addressing specific dietary needs.
Culinary Innovations
Culinary arts benefit significantly from 3D food printing. Chefs utilize this technology to craft intricate designs that elevate presentation and artistry in dishes. Customized pasta shapes and unique dessert forms illustrate how creativity meets functionality. Restaurants gain a competitive edge by offering visually stunning and personalized options. This method allows for the fusion of flavors and textures, creating meals that cater to individual preferences. 3D printing even opens doors for experimenting with new ingredient combinations, creating innovative dishes that surprise and delight diners. Each print represents not just food but an experience, transforming meals into edible artworks.
Medical and Nutritional Uses
3D food printing plays a pivotal role in nutrition and healthcare. By personalizing food according to nutritional needs, it addresses dietary restrictions effectively. This technology allows for precise control over ingredients, ensuring important nutrients are included. Patients with specific health conditions benefit from customized meals that cater to their dietary requirements. For example, modified textures can assist those with swallowing difficulties. Furthermore, it can produce fortified foods that improve overall health outcomes, particularly for vulnerable populations. 3D printing enables healthcare providers to collaborate with nutritionists, creating tailored meal plans that optimize well-being. The intersection of food technology and medicine presents promising possibilities for improving patient care.
Challenges and Future of 3D Food Printing
Developing 3D food printing faces several challenges. One major hurdle involves material limitations. Not all ingredients can be adapted for use in 3D printers, which constrains the variety of dishes that can be created. Customization of extruders also remains a concern, as different materials require specific nozzle sizes and flow rates.
Cost is another significant barrier in the industry. Initial investments for 3D food printing technology often exceed budget constraints for smaller establishments. Operational expenses, including maintenance and ingredient variations, add further financial pressure.
Regulatory considerations pose additional challenges. Food safety regulations must adapt to new technologies, meaning manufacturers need to ensure compliance with local and international food standards. Ensuring food safety and quality in 3D printed items is paramount to gaining consumer trust.
Despite these challenges, the future of 3D food printing appears promising. Innovative solutions continue to emerge, addressing material diversity and enhancing the capabilities of printers. Researchers are actively experimenting with new edible materials, broadening the scope of 3D printed cuisine.
Growth in healthcare applications drives further exploration of this technology. Personalized nutritional solutions have become crucial for addressing dietary needs. Future advancements may enable finer control over nutritional composition, enhancing health outcomes for patients.
Increased interest from culinary schools fosters creative exploration. Students engage with technology, gaining skills that prepare them for future culinary landscapes. As awareness and demand rise, the technology’s reach expands across industries, from restaurants to home kitchens.
Ultimately, 3D food printing stands at the intersection of culinary innovation and technological advancement. Its potential to revolutionize food production, reduce waste, and enhance culinary artistry presents exciting opportunities for chefs and consumers alike.
3D food printing is revolutionizing the culinary landscape by merging technology with creativity. This innovative approach not only enhances the visual appeal of dishes but also caters to individual dietary preferences and sustainability goals. As chefs and food designers embrace this technology, they unlock endless possibilities for unique culinary experiences.
The intersection of food and technology continues to evolve, promising a future where personalized nutrition and artistic expression coexist. With ongoing advancements addressing challenges and expanding material options, 3D food printing is poised to redefine how meals are crafted and enjoyed. The journey into this new frontier is just beginning, and its potential is limited only by imagination.